1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride CAS#: 79917-90-1; ChemWhat Code: 70108
Identification
| Patent Information | ||
| Patent ID | Title | Publication Date |
| CN118063314 | Method for preparing dimethyl 1, 4-cyclohexanedicarboxylate through dimethyl terephthalate hydrogenation | 2024 |
| US2022/48864 | METHOD FOR PRODUCING AMIDATE COMPOUND, AND AMIDATE COMPOUND | 2022 |
| CN113024414 | Method for efficiently synthesizing fluorine-containing compound | 2021 |
| CN110885314 | Metal ionic liquid, preparation method thereof, and application of metal ionic liquid in catalyzing cycloaddition reaction of carbon dioxide to prepare cyclic carbonate | 2020 |
| JP2019/199419 | METHOD FOR PRODUCING ISOCYANATE | 2019 |
Physical Data
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
| Melting Point, °C |
| 70 |
| 60 |
| 65 – 67 |
| 66.84 |
| 68 – 69 |
| 65 – 67 |
| 66 – 68 |
| Density, g·cm-3 | Measurement Temperature, °C |
| 90 | |
| 0.00107998 | 24.99 |
| 1.05468 | 74.99 |
| 1.0602 | 64.99 |
| 1.08 | 25 |
| 1.207 | 26 |
| Description (Association (MCS)) | Solvent (Association (MCS)) | Temperature (Association (MCS)), °C | Partner (Association (MCS)) |
| Association with compound | levofloxacin | ||
| Association with compound | water-d2 | Ahen egg white lysozyme | |
| Association with compound | sodium 2-(4-isobutylphenyl)propionate | ||
| Association with compound | 24.99 | acetonitrile | |
| Association with compound | 24.99 | acetonitrile, methanol | |
| Association with compound | calf thymus DNA | ||
| Association with compound | boehmite |
Spectra
| Description (NMR Spectroscopy) | Nucleus (NMR Spectroscopy) | Solvents (NMR Spectroscopy) |
| Chemical shifts | 13C | chloroform-d1 |
| Chemical shifts | 13C | cdimethylsulfoxide-d6 |
| Chemical shifts, Spectrum | 1H | chloroform-d1 |
| Chemical shifts | 1H | chloroform-d1 |
| Spectrum | 1H | |
| Chemical shifts | 1H | chloroform-d1 |
| Chemical shifts | 1H | water-d2 |
| Description (IR Spectroscopy) | Solvent (IR Spectroscopy) |
| Spectrum | |
| Bands, Spectrum | potassium bromide |
| ATR (attenuated total reflectance), Bands, Spectrum | |
| Bands, Spectrum |
| Description (UV/VIS Spectroscopy) | Solvent (UV/VIS Spectroscopy) | Absorption Maxima (UV/VIS), nm |
| Spectrum | ||
| Spectrum | 211 | |
| Spectrum | ||
| Spectrum | water | 380 |
| 211 | ||
| Spectrum | 220 | |
| aq. phosphate buffer | 210 |
Route of Synthesis (ROS)
| Conditions | Yield |
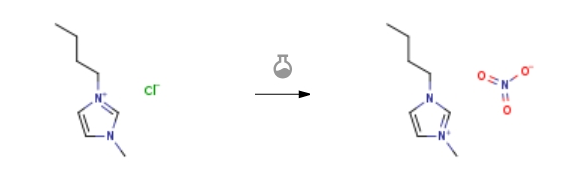
| With silver nitrate In water at 60℃; for 1h; Experimental Procedure Synthesis and characterization of BMImNO<sub>3</sub> BMImCl (17.4 g,0.1 mol) was dissolved in distilled water (60 mL), then AgNO3 (16.9 g, 0.1 mol) was added. After stirring at 60 oC for 1 h, this mixture was filtered under reduced pressure, and filtrate was concentrated by rotary evaporation. The light yellow oil was dried at 70 oC in air, obtained in 96% yield (19.3 g). | 96% |
| With sodium nitrate In dichloromethane at 20℃; for 24h; Experimental Procedure 2 Synthesis of [bmim][NO3], [bmim][SCN] and [bmim][N(CN)2] General procedure: According to literature procedures [40], NaNO3(1.1 eq), KSCN(1.2 eq) or NaN(CN)2 (1.1 eq) was added to a solution of [Bmim][Cl](1 eq) in dichloromethane and stirred for 24 h at room temperature.The suspension was filtered to remove the produced NaCl andunreacted NaNO3, KSCN and NaN(CN)2 salts. The organic phase was repeatedlywashed with small volume of water until no precipitation ofAgCl occurred in the aqueous phase on addition of AgNO3 solution.Then solvent was removed in vacuo and the synthesized IL was stirredwith activated charcoal for 6 h, removing the solvent gives[bmim][NO3], [bmim][SCN] and [bmim][N(CN)2] with 82%, 74% and85% yields, respectively. | 82% |
| With silver nitrate In water at 20℃; for 1h; Experimental Procedure The 1-butyl-3-methyl-imidazolium nitrate is synthesised by addition of an aqueous solution of silver nitrate (0.25 Mol in 100 ml water) to a stirring aqueous solution of 1-butyl-3-methyl-imidazolium chloride (commercially available from Solvent Innovation GmbH, AlarichstraRe 14-16,50679 Koln, Germany) (0.25 Mol in 100 ml water) at room temperature and allowed to react for one hour. The silver chloride formed is removed by filtration over a glass filter (porosity: P4). The water is removed from the 1-butyl-3-methyl-imidazolium nitrate solution by evaporation. The 1-butyl-3-methyl- imidazolium nitrate product is then dried in vacuo for three hours at 70 °C. | 99% |
| With silver nitrate In water |
Safety and Hazards
| Pictogram(s) |  |
| Signal | Danger |
| GHS Hazard Statements | H301 (100%): Toxic if swallowed [Danger Acute toxicity, oral] H315 (100%): Causes skin irritation [Warning Skin corrosion/irritation] H319 (100%): Causes serious eye irritation [Warning Serious eye damage/eye irritation] |
| Precautionary Statement Codes | P264, P264+P265, P270, P280, P301+P316, P302+P352, P305+P351+P338, P321, P330, P332+P317, P337+P317, P362+P364, P405, and P501 (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
Other Data
| Druglikeness | |
| Lipinski rules component | |
| Molecular Weight | 174.673 |
| logP | 3.086 |
| HBA | 1 |
| HBD | 0 |
| Matching Lipinski Rules | 4 |
| Veber rules component | |
| Polar Surface Area (PSA) | 38.81 |
| Rotatable Bond (RotB) | 3 |
| Matching Veber Rules | 2 |
| Use Pattern |
| BASIONIC(TM) ST 70 is an innovative approach to enhancing low-quality cellulose through a dual mechanism that operates at both the nanoscale and molecular levels. Molecular-Level Enhancement: To further improve the performance of low-quality cellulose, BASIONIC™ introduces a small quantity of high-degree polymerized cellulose. This addition strengthens the entangled network of cellulose molecular chains, promoting greater cohesion among the fibers and enhancing the material’s mechanical stability. By increasing the density and resilience of the cellulose molecular network, this method enhances the overall durability and performance of low-quality cellulose. This molecular-level enhancement ensures that even lower-grade cellulose can achieve improved properties without compromising on flexibility or tensile strength, making it suitable for broader industrial applications. Nanoscale Reinforcement: By employing ionic liquids with selective dissolution properties, BASIONIC™ can effectively dissolve cellulose while preserving cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) in the raw material as an in-situ reinforcing phase. These CNCs possess exceptional mechanical properties and, when retained within the cellulose matrix, act as a strengthening component, improving the material’s structural integrity at the nanoscale. This approach provides a practical solution to enhance lower-grade cellulose, allowing it to gain properties closer to that of higher-quality materials by utilizing CNCs for reinforcement. The precision of ionic liquid technology is key here, enabling selective dissolution and retention of CNCs in a way that traditional methods cannot match. |
Buy Reagent | |
| No reagent supplier? | Send quick inquiry to ChemWhat |
| Want to be listed here as a reagent supplier? (Paid service) | Click here to contact ChemWhat |
Approved Manufacturers | |
| Want to be listed as an approved manufacturer (Requires approvement)? | Please download and fill out this form and send back to approved-manufacturers@chemwhat.com |
Contact Us for Other Help | |
| Contact us for other information or services | Click here to contact ChemWhat |