Anti-C-Reactive Protein (CRP) Antibody; ChemWhat Code: 1394040
Antigen
| Name | C-Reactive Protein (CRP) |
| Synonyms | CRP; PTX1; C-reactive protein; pentraxin-related; pentraxin 1 |
Description
| Name | Anti-C-Reactive Protein (CRP) Antibody |
| Synonyms | C-Reactive Protein; C-reactive protein, pentraxin-related; CRP; MGC88244; pentraxin 1 |
| Host | Mouse; Goat; Rabbit |
| Reactivity | All species |
| Antibody Product Type | Primary |
| Use | Detection; Capture |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated; Biotin; APC; Alkaline Phosphatase (AP); FITC; HRP; PE |
| Specifity | The antibody is raised against CRP. It has been selected for its ability to recognize CRP. |
| Application | ELISA; Immunohistochemistry (IHC); Western Blotting (WB); Immunofluorescence (fixed cells) (IF/ICC); Immunoprecipitation (IP); Cell-ELISA (cELISA); Immunoassay (IA); Immunocytochemistry (ICC) |
Properties
| Form | Liquid/Lyophilized |
| Handling | The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use. |
| Storage Condition | Store at 4°C for frequent use. Stored at -20°C in a manual defrost freezer for a year without detectable loss of activity. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Clonality | Monoclonal/Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
Safety Information
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| Flash Point(F) | Not applicable |
| Flash Point(C) | Not applicable |
Images
| Anti-C-Reactive Protein (CRP) Antibody in WB | 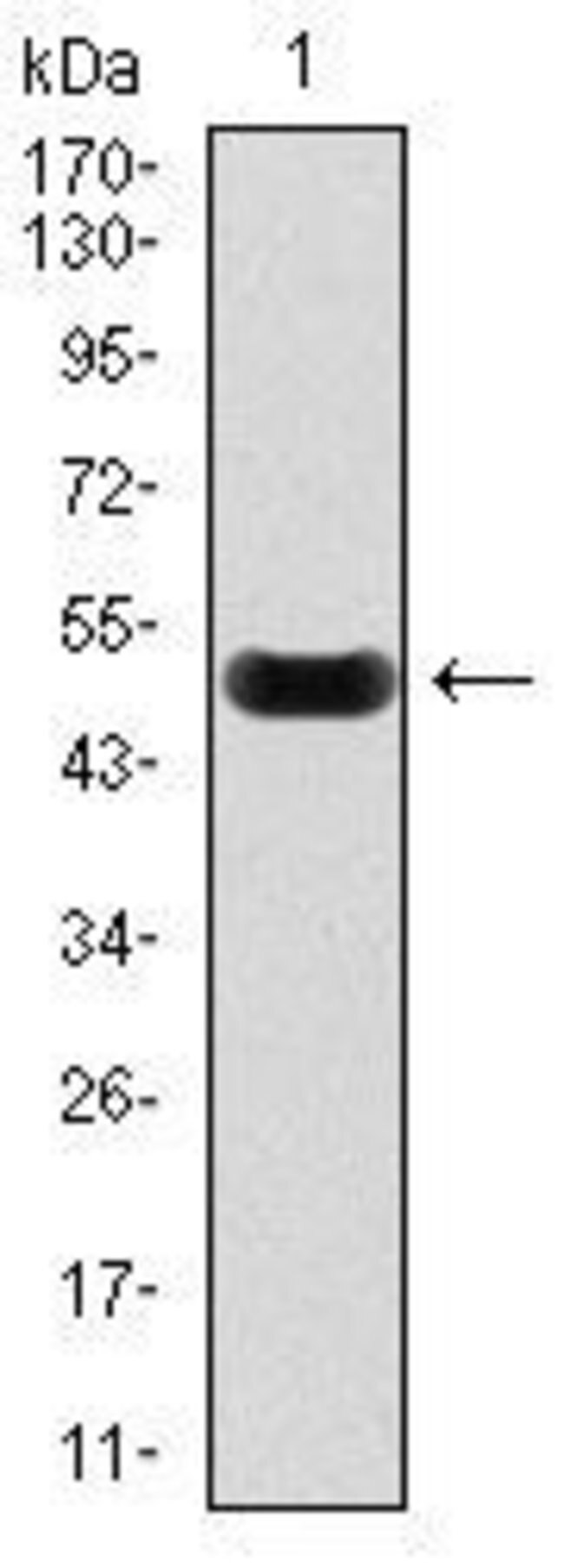 |
| Anti-C-Reactive Protein (CRP) Antibody in IHC | 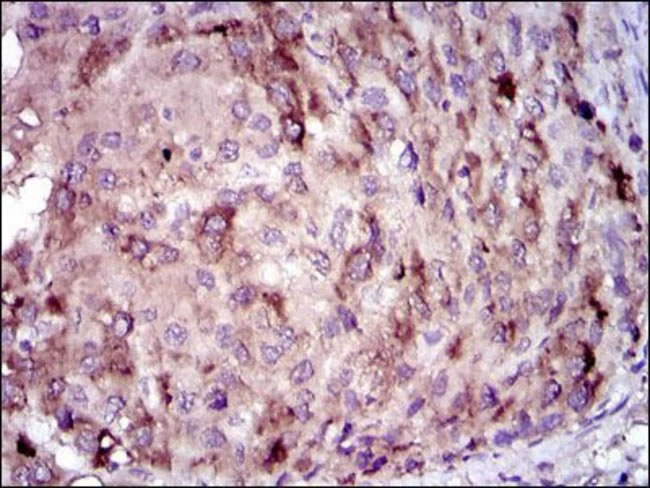 |
| Anti-C-Reactive Protein (CRP) Antibody in flow |  |
Other Info
| About the antigen | CRP is a plasma protein involved in host defense by promoting agglutination, bacterial capsular swellling, phagocytosis and complement fixation through its calcium-dependent binding to phosphorylcholine. It also scavenges nuclear material released from damaged circulating cells. The concentration of CRP in plasma increases greatly during acute phase response to tissue injury, infection or other inflammatory stimuli. CRP has two isoforms produced by alternative splicing. CRP is synthesized by the liver in response to factors released by fat cells. It is a member of the pentraxin family of proteins. The levels of CRP rise in response to inflammation. Human C-reactive protein (CRP) is the classical acute phase reactant, the circulating concentration of which rises rapidly and extensively in a cytokine-mediated response to tissue injury, infection and inflammation. Serum CRP values are routinely measured, empirically, to detect and monitor many human diseases. However, CRP is likely to have important host defence, scavenging and metabolic functions through its capacity for calcium-dependent binding to exogenous and autologous molecules containing phosphocholine (PC) and then activating the classical complement pathway. CRP may also have pathogenic effects and the recent discovery of a prognostic association between increased CRP production and coronary atherothrombotic events is of particular interest. |
Related Chemicals
Buy Reagent | |
| No reagent supplier? | Send quick inquiry to ChemWhat |
| Want to be listed here as a reagent supplier? (Paid service) | Click here to contact ChemWhat |
Approved Manufacturers | |
| Want to be listed as an approved manufacturer (Requires approvement)? | Please download and fill out this form and send back to approved-manufacturers@chemwhat.com |
Contact Us for Other Help | |
| Contact us for other information or services | Click here to contact ChemWhat |