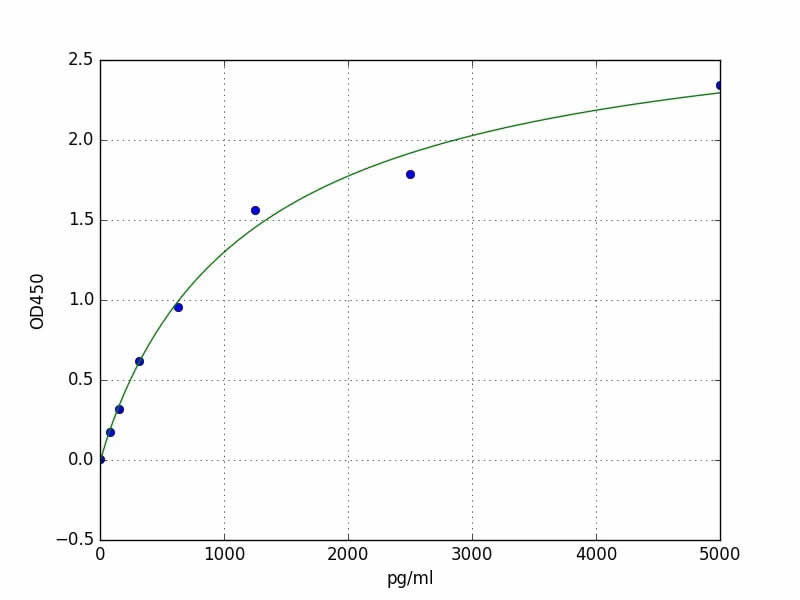
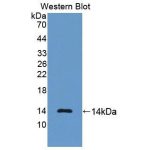
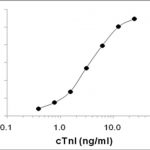
Anti-CKMB (CK-MB, one isoenzyme of CK, creatine kinase CAS#: 9001-15-4, EC 2.7.3.2) antibody; ChemWhat Code: 1394000
Antigen
| Name | CK-MB |
| Synonyms | CK MB; CPK MB; creatine kinase MB; 9001-15-4; 2.7.3.2 |
Description
| Name | Anti-CKMB antibody |
| Synonyms | KMB antibody, Anti-CKMB antibody, Creatine Kinase-MB Isoenzyme antibody, CK-MB antibody |
| Host | Mouse; Goat; Rabbit |
| Reactivity | All species |
| Antibody Product Type | Primary |
| Use | Detection; Capture |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated; Biotin; APC; Alkaline Phosphatase (AP); FITC; HRP; PE |
| Specifity | Recognizes CK-MB, one isoenzyme of CK, creatine kinase. |
| Application | ELISA; Immunohistochemistry (IHC); Western Blotting (WB); Immunofluorescence (fixed cells) (IF/ICC); Immunoprecipitation (IP); Cell-ELISA (cELISA); Immunoassay (IA); Immunocytochemistry (ICC) |
Properties
| Form | Liquid/Lyophilized |
| Handling | The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use. |
| Storage Condition | Store at 4°C for frequent use. Stored at -20°C in a manual defrost freezer for a year without detectable loss of activity. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Clonality | Monoclonal/Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
Safety Information
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | WGK 3 |
| Flash Point(F) | Not applicable |
| Flash Point(C) | Not applicable |
Images
Other Info
| About the antigen | Creatine kinase (CK) is an enzyme expressed by various tissues and cell types. CK catalyses the conversion of creatine and consumes adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to create phosphocreatine and adenosine diphosphate (ADP). This CK enzyme reaction is reversible, such that also ATP can be generated from PCr and ADP. In the cells, the “cytosolic” CK enzymes consist of two subunits, which can be either B (brain type) or M (muscle type). There are, therefore, three different isoenzymes: CK-MM, CK-BB and CK-MB. |
| Clinical Diagnosis | Patients with skeletal muscle disease, acute muscle exertion, chronic renal failure, and cocaine use can have elevations in levels of CK-MB in the absence of infarction. In order to distinguish true positive elevations (secondary to myocardial injury) from the false positive elevations (due to skeletal muscle injury), the measurement of CK-MB as a percentage of total CK has been used to calculate relative index. A CK-MB to CK ratio of > 6% is reported to be specific for myocardial injury, whereas a ratio of < 6% is consistent with skeletal muscle damage or non-cardiac causes. |
Related Chemicals
Buy Reagent | |
| No reagent supplier? | Send quick inquiry to ChemWhat |
| Want to be listed here as a reagent supplier? (Paid service) | Click here to contact ChemWhat |
Approved Manufacturers | |
| Want to be listed as an approved manufacturer (Requires approvement)? | Please download and fill out this form and send back to approved-manufacturers@chemwhat.com |
Contact Us for Other Help | |
| Contact us for other information or services | Click here to contact ChemWhat |