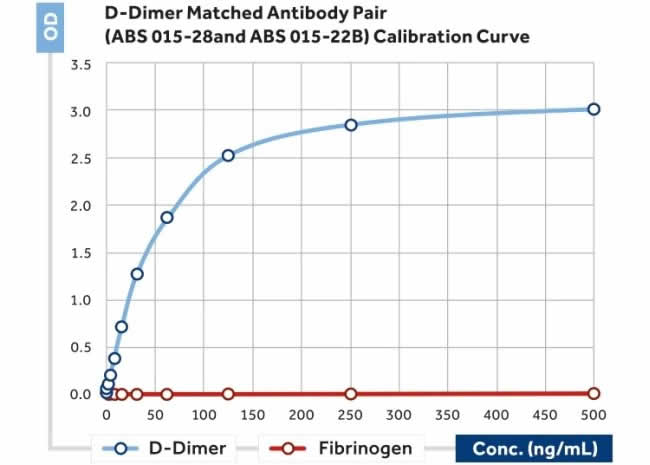
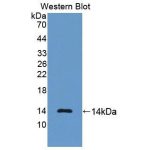
Anti-D-Dimer antibody; ChemWhat Code: 1394014
Antigen
| Name | D-Dimer |
| Synonyms | Fibrin degradation fragment; Fragment D-dimer |
Description
| Name | Anti-D-Dimer antibody |
| Synonyms | D-dimer antibody, Anti-D-dimer antibody, Ddimer antibody, D dimer antibody |
| Host | Mouse; Goat; Rabbit |
| Reactivity | All species |
| Antibody Product Type | Primary |
| Use | Detection; Capture |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated; Biotin; APC; Alkaline Phosphatase (AP); FITC; HRP; PE |
| Specifity | It recognises epitopes that reside between amino acids 86 and 302 in the gamma-chain of fragment D chains of fibrinogen (Fragment D) and other cross-linked fibrin degradation products containing D-Dimer, but no reactivity with Fragment D or E, fibrinogen or fibrinogen degradation products. |
| Application | ELISA; Immunohistochemistry (IHC); Western Blotting (WB); Immunofluorescence (fixed cells) (IF/ICC); Immunoprecipitation (IP); Cell-ELISA (cELISA); Immunoassay (IA); Immunocytochemistry (ICC) |
Properties
| Form | Liquid/Lyophilized |
| Handling | The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use. |
| Storage Condition | Store at 4°C for frequent use. Stored at -20°C in a manual defrost freezer for a year without detectable loss of activity. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Clonality | Monoclonal/Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
Safety Information
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| Flash Point(F) | Not applicable |
| Flash Point(C) | Not applicable |
Images
Other Info
| About the antigen | D-dimer (or D dimer) is a fibrin degradation product (or FDP), a small protein fragment present in the blood after a blood clot is degraded by fibrinolysis. It is so named because it contains two D fragments of the fibrin protein joined by a cross-link. |
| Clinical Diagnosis | D-dimer concentration may be determined by a blood test to help diagnose thrombosis. Since its introduction in the 1990s, it has become an important test performed in subjects with suspected thrombotic disorders. While a negative result practically rules out thrombosis, a positive result can indicate thrombosis but does not rule out other potential causes. Its main use, therefore, is to exclude thromboembolic disease where the probability is low. In addition, it is used in the qualification of the blood disorder disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Elevated DDimer levels are found in cases of DIC, deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) but other circumstances may also lead to high levels such as old age, pregnancy, cancer, liver disease and infection. Elevated concentrations of D-dimer can be observed in a variety of diseases and during fibrinolytic therapy (e.g. with streptokinase and t-PA). In all diseases with an elevated activation (e.g. thromboembolism and DIC) hyperfibrinolysis has been observed as the counter reaction to the elevated fibrin formation. D-dimer is a marker for this hyperfibrinolysis. Elevated D-dimer concentrations thus can be observed in thromboembolic diseases (pulmonary embolism, deep venous thrombosis), leukaemia and sepsis, intra- and postoperative, in physical and mental stress and during extra corporeal circulation. |
Related Chemicals
Buy Reagent | |
| No reagent supplier? | Send quick inquiry to ChemWhat |
| Want to be listed here as a reagent supplier? (Paid service) | Click here to contact ChemWhat |
Approved Manufacturers | |
| Want to be listed as an approved manufacturer (Requires approvement)? | Please download and fill out this form and send back to approved-manufacturers@chemwhat.com |
Contact Us for Other Help | |
| Contact us for other information or services | Click here to contact ChemWhat |