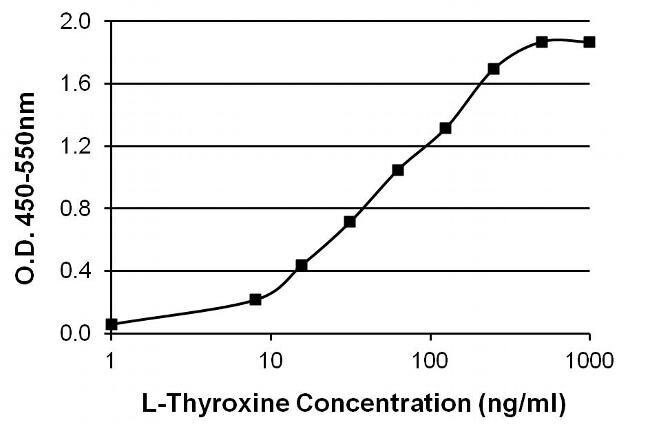
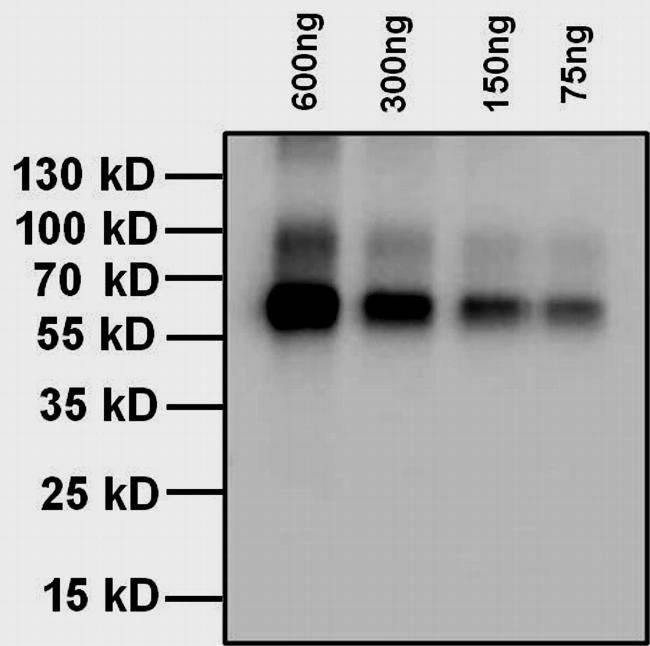
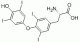
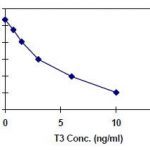
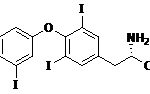
Anti-T4 (thyroxine T4 CAS#: 51-48-9) Antibody; ChemWhat Code: 1393913
Antigen
| Name | Thyroxine T4 |
| Synonyms | T4; Thyroxine; 51-48-9; |
Description
| Name | Anti-Thyroxine (T4) Antibody |
| Synonyms | Anti-T4 Antibody; Anti-Thyroxine antibody; L-Thyroxine (T4) antibody |
| Host | Mouse; Goat; Rabbit |
| Reactivity | All species |
| Antibody Product Type | Primary |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated; Biotin; APC; Alkaline Phosphatase (AP); FITC; HRP; PE |
| Specifity | Recognizes Thyroxine, also known as T4, the major hormone secreted by the follicular cells of the thyroid gland. Its main role is to regulate metabolic processes in the body such as heart rate, along with Triiodothyronine (T3). T4 is involved in thyroid disorders, such as hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. |
| Application | ELISA; Immunohistochemistry (IHC); Western Blotting (WB); Immunofluorescence (fixed cells) (IF/ICC); Immunoprecipitation (IP); Cell-ELISA (cELISA); Immunoassay (IA); Immunocytochemistry (ICC) |
Properties
| Form | Liquid/Lyophilized |
| Handling | The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use. |
| Storage Condition | Store at 4°C for frequent use. Stored at -20°C in a manual defrost freezer for a year without detectable loss of activity. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Clonality | Monoclonal/Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
Safety Information
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | WGK 3 |
| Flash Point(F) | Not applicable |
| Flash Point(C) | Not applicable |
Images
Other Info
| About the antigen | Antibodies against thyroxine (T4) were detected in a patient of systemic lupus erythematosus associated with chronic thyroiditis and a patient with primary myxedema. Both patients were clincally hypothyroid with elevated serum TSH. Serum T4 values measured with solid phase radioimmunoassay were very high (over 25ug/dl), but were undetected with polyethylene glycol separation method. On the extraction of the sera with ethanol, the concordant low values of T4 were obtained with both radioimmunoassay methods and these values were compatible with clinical findings and serum TSH levels. The thyroid hormones, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), are tyrosine-based hormones produced by the thyroid gland primarily responsible for regulation of metabolism. An important component in the synthesis of thyroid hormones is iodine. The major form of thyroid hormone in the blood is thyroxine (T4), which has a longer half life than T3. |
Related Chemicals
Buy Reagent | |
| No reagent supplier? | Send quick inquiry to ChemWhat |
| Want to be listed here as a reagent supplier? (Paid service) | Click here to contact ChemWhat |
Approved Manufacturers | |
| Want to be listed as an approved manufacturer (Requires approvement)? | Please download and fill out this form and send back to approved-manufacturers@chemwhat.com |
Contact Us for Other Help | |
| Contact us for other information or services | Click here to contact ChemWhat |