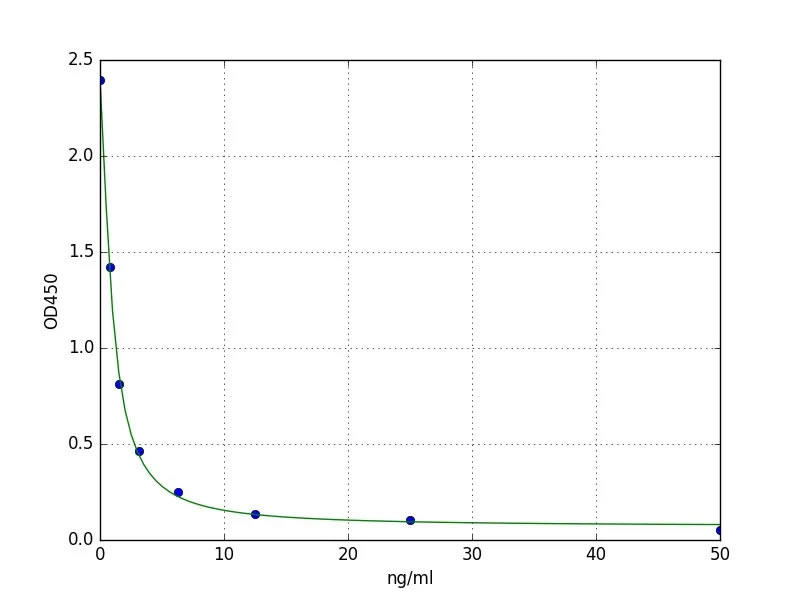
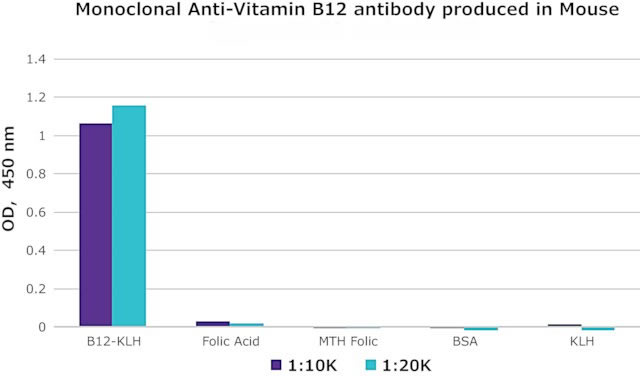
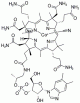
Anti-Vitamin B12 (Vitamin B12, VB12, CAS#: 68-19-9) antibody; ChemWhat Code: 1393847
Antigen
| Name | Vitamin B12 |
| Synonyms | Vitamin B12; VB12; Alpha (5 6 Dimethylbenzimidazolyl)cyanocobamide; Cyanocobalamin; 68-19-9 |
Description
| Name | Anti-Vitamin B12 antibody |
| Vitamin B12 antibody; Anti-Vitamin B12 antibody; Cyanocobalamin antibody; Vitamin B12; Vitamin B -12 antibody; Vitamin B 12; Vitamin B -12; Vitamin B 12 antibody; VB12 | |
| Host | Mouse; Goat; Rabbit |
| Antibody Product Type | Primary |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated; Biotin; APC; Alkaline Phosphatase (AP); FITC; HRP; PE |
| Specifity | Recognizes Vitamin B12: 100%. This antibody recognizes both free and conjugated of Vitamin B12 |
| Application | ELISA; Immunohistochemistry (IHC); Western Blotting (WB); Immunofluorescence (fixed cells) (IF/ICC); Immunoprecipitation (IP); Cell-ELISA (cELISA); Immunoassay (IA); Immunocytochemistry (ICC) |
Properties
| Form | Liquid/Lyophilized |
| Handling | The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use. |
| Storage Condition | Store at 4°C for frequent use. Stored at -20°C in a manual defrost freezer for a year without detectable loss of activity. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Clonality | Monoclonal/Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
Safety Information
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | WGK 2 |
| Flash Point(F) | Not applicable |
| Flash Point(C) | Not applicable |
Images
Other Info
| About the antigen | Vitamin B12, vitamin B12, VB 12 or vitamin B-12, also called cobalamin, is a water soluble vitamin with a key role in the normal functioning of the brain and nervous system, and for the formation of blood. It is normally involved in the metabolism of every cell of the human body, especially affecting DNA synthesis and regulation, but also fatty acid synthesis and energy production. Vitamin B12 is a member of the vitamin B complex. It contains cobalt, and so is also known as cobalamin. It is exclusively synthesised by bacteria and is found primarily in meat, eggs and dairy products. There has been considerable research into proposed plant sources of vitamin B12. Fermented soya products, seaweeds, and algae such as spirulina have all been suggested as containing significant B12. However, the present consensus is that any B12 present in plant foods is likely to be unavailable to humans and so these foods should not be relied upon as safe sources. Vitamin B12 is necessary for the synthesis of red blood cells, the maintenance of the nervous system, and growth and development in children. Deficiency can cause anaemia. Vitamin B12 neuropathy, involving the degeneration of nerve fibres and irreversible neurological damage, can also occur. |
Related Chemicals
Buy Reagent | |
| No reagent supplier? | Send quick inquiry to ChemWhat |
| Want to be listed here as a reagent supplier? (Paid service) | Click here to contact ChemWhat |
Approved Manufacturers | |
| Want to be listed as an approved manufacturer (Requires approvement)? | Please download and fill out this form and send back to approved-manufacturers@chemwhat.com |
Contact Us for Other Help | |
| Contact us for other information or services | Click here to contact ChemWhat |