Benzophenone hydrazone CAS#: 5350-57-2; ChemWhat Code: 63598
Identification
| Product Name | Benzophenone hydrazone |
| IUPAC Name | benzhydrylidenehydrazine |
| Molecular Structure | 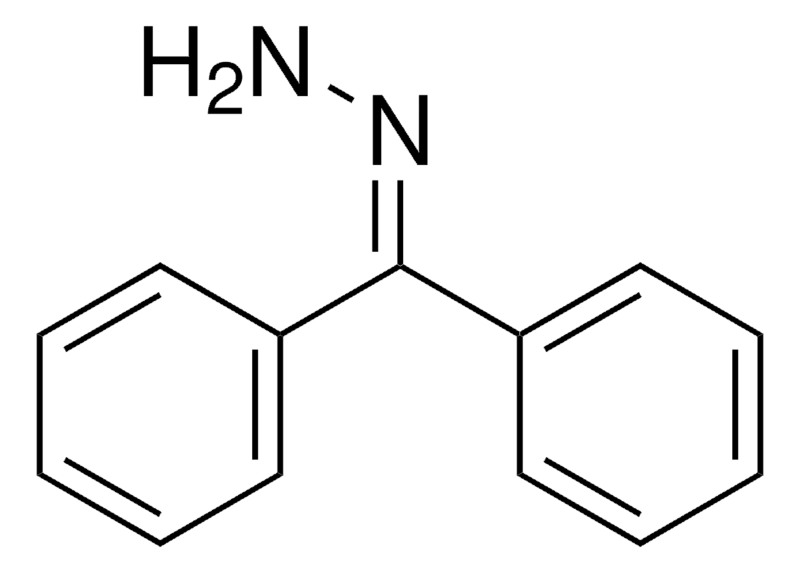 |
| CAS Registry Number | 5350-57-2 |
| EINECS Number | 226-321-8 |
| MDL Number | MFCD00007624 |
| Beilstein Registry Number | 1910177 |
| Synonyms | benzophenone hydrazone(diphenylmethylene)hydrazinediphenylmethanone hydrazone(diphenylmethylidene)hydrazine1-(diphenylmethylene)hydrazinebenzhydrylidene hydrazine(diphenylmethylene)hydrazone |
| Molecular Formula | C13H12N2 |
| Molecular Weight | 196.253 |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C13H12N2/c14-15-13(11-7-3-1-4-8-11)12-9-5-2-6-10-12/h1-10H,14H2 |
| InChI Key | QYCSNMDOZNUZIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Canonical SMILES | NN=C(c1ccccc1)c1ccccc1 |
| Patent Information | ||
| Patent ID | Title | Publication Date |
| CN109651376 | Synthetic method of azepino [5,4, 3-cd] indole-6-ketone compound | 2019 |
| CN105541660 | Arylsalicylaldehyde-diphenyl-azine hydrazine compound as well as preparation and application | 2016 |
Physical Data
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
| Solubility | No data available |
| Flash Point | No data available |
| Refractive index | No data available |
| Sensitivity | No data available |
| Melting Point, °C | Solvent (Melting Point) |
| 98 – 99 | |
| 95 – 98 | |
| 94 – 95 | |
| 96 – 97 | ethanol |
| Boiling Point, °C | Pressure (Boiling Point), Torr |
| 225 – 230 | 55 |
| Description (Association (MCS)) | Solvent (Association (MCS)) | Temperature (Association (MCS)), °C | Partner (Association (MCS)) |
| Stability constant of the complex with … | H2O | 20 | Th(4+) |
| Association with compound | |||
| Enthalpy of association |
Spectra
| Description (NMR Spectroscopy) | Nucleus (NMR Spectroscopy) | Solvents (NMR Spectroscopy) | Temperature (NMR Spectroscopy), °C | Frequency (NMR Spectroscopy), MHz |
| Chemical shifts, Spectrum | 1H | chloroform-d1 | 25 | |
| Chemical shifts, Spectrum | 13C | chloroform-d1 | 25 | |
| Chemical shifts | 1H | chloroform-d1 | 25 | 300 |
| Description (IR Spectroscopy) | Solvent (IR Spectroscopy) |
| Bands | potassium bromide |
| IR | nujol |
| Description (Mass Spectrometry) |
| high resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS), electrospray ionisation (ESI), spectrum |
| high resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS), electrospray ionisation (ESI), liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LCMS), time-of-flight mass spectra (TOFMS), spectrum |
| electron impact (EI), spectrum |
| electron impact (EI), high resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS), spectrumpectrum |
| high resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS), electrospray ionisation (ESI), spectrum |
| Description (UV/VIS Spectroscopy) | Solvent (UV/VIS Spectroscopy) | Absorption Maxima (UV/VIS), nm | Ext./Abs. Coefficient, l·mol-1cm-1 |
| Absorption maxima | 271, 300 | 12882, 10 | |
| Spectrum | neat (no solvent, solid phase) | 250, 309, 365 | |
| Absorption maxima | CCl4 | 288 | 24000 |
| Absorption maxima | dioxane | 278 | 11500 |
Route of Synthesis (ROS)
| Conditions | Yield |
| With palladium diacetate; 4,5-bis(diphenylphosphino)-9,9-dimethylxanthene; sodium t-butanolate In toluene at 80℃; for 1.5h; Arylation; | 98% |
| With sodium hydroxide; 2-(dicyclohexylphosphino)-2′-methylbiphenyl; palladium diacetate In tert-Amyl alcohol at 103℃; | 97% |
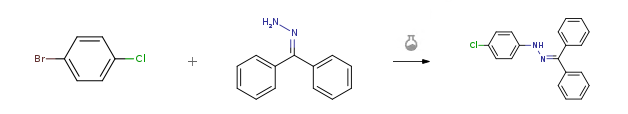
| Stage #1: bromochlorobenzene With sodium hydroxide In tert-Amyl alcohol Heating; Stage #2: benzophenone hydrazone With 2-(dicyclohexylphosphino)-2′-methylbiphenyl; palladium diacetate In tert-Amyl alcohol at 103℃; | 97% |
Safety and Hazards
| Pictogram(s) |    |
| Signal | Danger |
| GHS Hazard Statements | H301 (88.9%): Toxic if swallowed [Danger Acute toxicity, oral] H317 (88.9%): May cause an allergic skin reaction [Warning Sensitization, Skin] H401 (11.1%): Toxic to aquatic life [Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard] H411 (88.9%): Toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects [Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard] Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. |
| Precautionary Statement Codes | PP261, P264, P270, P272, P273, P280, P301+P316, P302+P352, P321, P330, P333+P317, P362+P364, P391, P405, and P501 (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
Other Data
| Transportation | NONH for all modes of transport |
| Under the room temperature and away from light | |
| HS Code | No data available |
| Storage | Under the room temperature and away from light |
| Shelf Life | 2 years |
| Market Price | USD |
| Druglikeness | |
| Lipinski rules component | |
| Molecular Weight | 196.252 |
| logP | 3.259 |
| HBA | 2 |
| HBD | 1 |
| Matching Lipinski Rules | 4 |
| Veber rules component | |
| Polar Surface Area (PSA) | 38.38 |
| Rotatable Bond (RotB) | 2 |
| Matching Veber Rules | 2 |
| Use Pattern |
| Organic synthesis intermediates Benzophenone hydrazone is often used as an intermediate in organic synthesis, especially in the preparation of heterocyclic compounds and pharmaceutical compounds. Its hydrazone group ( – C=N – NH₂) can undergo condensation reactions and cyclization reactions under certain conditions to generate more diverse compounds, such as indole, pyrazole and other heterocyclic compounds, which have important uses in medicine and pesticides. |
| Drug development As a hydrazone compound, benzophenone hydrazone is used as a lead compound in medicinal chemistry. Studies have shown that hydrazone compounds have potential in the development of antibacterial, antiviral, anticancer and anti-inflammatory drugs. By modifying its molecular structure, it is possible to obtain new drug candidates with biological activity. |
| Metal chelators Benzophenone hydrazone can be used as a metal chelator, especially in analytical chemistry for the separation and detection of metal ions. It can form stable complexes with a variety of metal ions (such as copper, iron, and cobalt) for chromatographic separation and spectrophotometric detection. The complexes formed with metal ions can also be used for catalytic reactions to improve the efficiency of certain organic conversion reactions. |
| Light stabilizers and UV absorbers Due to the combination of its phenyl structure and hydrazone group, benzophenone hydrazone has a certain UV absorption capacity and can be used as a light stabilizer in plastics and polymer materials to extend their service life and prevent aging and degradation caused by UV irradiation. |
| Organic optoelectronic materials In the field of organic optoelectronics, hydrazone compounds may be used to develop organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) and organic photovoltaic cells (OPVs) materials due to their photoluminescent properties. The tunability of its structure makes it potentially a new type of optoelectronic functional material. |
Buy Reagent | |
| No reagent supplier? | Send quick inquiry to ChemWhat |
| Want to be listed here as a reagent supplier? (Paid service) | Click here to contact ChemWhat |
Approved Manufacturers | |
| Caming Pharmaceutical Ltd | http://www.caming.com/ |
| Want to be listed as an approved manufacturer (Requires approvement)? | Please download and fill out this form and send back to approved-manufacturers@chemwhat.com |
Contact Us for Other Help | |
| Contact us for other information or services | Click here to contact ChemWhat |