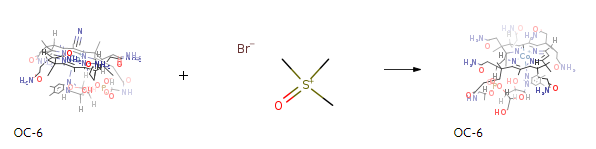
Stage #1: cyanocobalamin With sodium tetrahydroborate; cobalt(II) chloride In water; butanone at 30 – 50℃; for 1.66667 – 2.5h;
Stage #2: trimethyloxosulfonium bromide In water; butanone at 15 – 50℃;
Experimental Procedure
1; 2; 3; 4; 5; 6; 7; 8; 9 Example 1 Synthesis of Methylcobalamin
All the procedures in the present example were performed in the dark (under red light). To 65 ml of ion-exchanged water were added 5 g of cyanocobalamin, 0.35 g of cobalt chloride hexahydrate, and 3.75 ml of 2-butanone. After replacing the inside atmosphere of the system with nitrogen gas, the mixture was heated in a water bath, to which an aqueous solution of sodium borohydride (2 g/10 ml) was added dropwise under stirring at a bath temperature of 38°C over 60 minutes. After stirring for further 30 minutes as it was, an aqueous solution of trimethylsulfoxonium bromide (1.9 g/10 ml) was further added thereto over 30 minutes. The mixture was stirred for further 3 hours as it was, followed by stirring overnight at a bath temperature of 15°C. The resulting precipitates were collected by filtration and dried to give a crude product of the title compound. To the crude product was added a 50% acetone aqueous solution. After heating at 35°C, the mixture was adjusted to pH 7.0 with concentrated hydrochloric acid. Then, acetone was added dropwise thereinto and the mixture was stirred overnight. The precipitated crystals were collected by filtration and dried, to give the title compound in a yield of 85%. Physical properties of the resulting methylcobalamin: In a hydrochloric acid buffer (pH 2.0), UVmax was detected at 264-266, 303-307 and 459-462 nm. In a phosphate buffer (pH 7.0), UVmax was detected at 266-269, 341-344 and 520-524 nm. Referential values of UVmax (Merck Index, 12th edition) (0.1 N-HCl): 264, 304 and 462 nm (pH 7): 266, 342 and 522 nmExample 2 Synthesis of Methylcobalamin All the procedures in the present example were performed in the dark (under red light). To 260 ml of ion-exchanged water were added 20 g of cyanocobalamin, 1.4 g of cobalt chloride hexahydrate, and 15 ml of 2-butanone. After replacing the inside atmosphere of the system with nitrogen gas, the mixture was heated in a water bath, to which an aqueous solution of sodium borohydride (8 g/40 ml) was added dropwise under stirring at the internal temperature of 40°C over 70 minutes. After stirring for further 30 minutes as it was, an aqueous solution of trimethylsulfoxonium bromide (7.66 g/40 ml) was further added thereto over 30 minutes. The mixture was stirred for further 3 hours as it was, followed by stirring overnight at a bath temperature of 15°C. The resulting precipitates were collected by filtration and dried to give a crude product of the title compound. To the crude product was added a 50% acetone aqueous solution. After heating at 35°C, the mixture was adjusted to pH 7.0 with concentrated hydrochloric acid. Then, acetone was added dropwise thereinto and the mixture was stirred overnight. The precipitated crystals were collected by filtration and dried, to give the title compound in a yield of 85%.Example 3 Synthesis of Methylcobalamin All the procedures in the present example were performed in the dark (under red light). To 390 ml of ion-exchanged water were added 30 g of cyanocobalamin, 2.1 g of cobalt chloride hexahydrate, and 22.5 ml of 2-butanone. After replacing the inside atmosphere of the system with nitrogen gas, the mixture was heated in a water bath, to which an aqueous solution of sodium borohydride (12 g/60 ml) was added dropwise under stirring at the internal temperature of 40°C over 2 hours. After stirring for further 30 minutes as it was, an aqueous solution of trimethylsulfoxonium bromide (11.5 g/60 ml) was further added thereto over 30 minutes. The mixture was stirred for further 3 hours as it was, followed by stirring overnight at a bath temperature of 15°C. The resulting precipitates were collected by filtration and dried to give a crude product of the title compound. To the crude product was added a 50% acetone aqueous solution. After heating at 35°C, the mixture was adjusted to pH 7.0 with concentrated hydrochloric acid. Then, acetone was added dropwise thereinto and the mixture was stirred overnight. The precipitated crystals were collected by filtration and dried, to give the title compound in a yield of 88%.Example 4 Synthesis of Methylcobalamin All the procedures in the present example were performed in the dark (under red light). To 390 ml of ion-exchanged water were added 30 g of cyanocobalamin, 2.1 g of cobalt chloride hexahydrate, and 22.5 ml of 2-butanone. After replacing the inside atmosphere of the system with nitrogen gas, the mixture was heated in a water bath, to which an aqueous solution of sodium borohydride (12 g/60 ml) was added dropwise under stirring at the internal temperature of 40°C over 2 hours. After stirring for further 30 minutes as it was, an aqueous solution of trimethylsulfoxonium bromide (11.5 g/60 ml) was further added thereto over 30 minutes. The mixture was stirred for further 3 hours as it was, followed by stirring overnight at a bath temperature of 15°C. The resulting precipitates were collected by filtration and dried to give a crude product of the title compound. To the crude product was added a 50% acetone aqueous solution. After heating at 35°C, the mixture was adjusted to pH 7.0 with concentrated hydrochloric acid. Then, acetone was added dropwise thereinto and the mixture was stirred overnight. The precipitated crystals were collected by filtration and dried, to give the title compound in a yield of 87%.Example 5 Synthesis of Methylcobalamin All the procedures in the present example were performed in the dark (under red light). To 390 ml of ion-exchanged water were added 30 g of cyanocobalamin, 2.1 g of cobalt chloride hexahydrate, and 22.5 ml of 2-butanone. After replacing the inside atmosphere of the system with nitrogen gas, the mixture was heated in a water bath, to which an aqueous solution of sodium borohydride (12 g/60 ml) was added dropwise under stirring at the internal temperature of 50°C over 2 hours. After stirring for further 30 minutes as it was, an aqueous solution of trimethylsulfoxonium bromide (11.5 g/60 ml) was further added thereto over 30 minutes. The mixture was stirred for further 3 hours as it was, followed by stirring overnight at a bath temperature of 15°C. The resulting precipitates were collected by filtration and dried to give a crude product of the title compound. To the crude product was added a 50% acetone aqueous solution. After heating at 35°C, the mixture was adjusted to pH 7.0 with concentrated hydrochloric acid. Then, acetone was added dropwise thereinto and the mixture was stirred overnight. The precipitated crystals were collected by filtration and dried, to give the title compound in a yield of 88%.Example 6 Synthesis of Methylcobalamin All the procedures in the present example were performed in the dark (under red light). To 390 ml of ion-exchanged water were added 30 g of cyanocobalamin, 2.1 g of cobalt chloride hexahydrate, and 22.5 ml of 2-butanone. After replacing the inside atmosphere of the system with nitrogen gas, the mixture was heated in a water bath, to which an aqueous solution of sodium borohydride (12 g/60 ml) was added dropwise under stirring at the internal temperature of 50°C over 2 hours. After stirring for further 30 minutes as it was, an aqueous solution of trimethylsulfoxonium bromide (11.5 g/60 ml) was further added thereto over 30 minutes. The mixture was stirred for further 3 hours as it was, followed by stirring overnight at a bath temperature of 15°C. The resulting precipitates were collected by filtration and dried to give a crude product of the title compound. To the crude product was added a 50% acetone aqueous solution. After heating at 35°C, the mixture was adjusted to pH 7.0 with concentrated hydrochloric acid. Then, acetone was added dropwise thereinto and the mixture was stirred overnight. The precipitated crystals were collected by filtration and dried, to give the title compound in a yield of 87%.Example 7 Synthesis of Methylcobalamin All the procedures in the present example were performed in the dark (under red light). To 390 ml of ion-exchanged water were added 3 0 g of cyanocobalamin, 2.1 g of cobalt chloride hexahydrate, and 22.5 ml of 2-butanone. After replacing the inside atmosphere of the system with nitrogen gas, the mixture was heated in a water bath, to which an aqueous solution of sodium borohydride (12 g/60 ml) was added dropwise under stirring at the internal temperature of 30°C over 2 hours. After stirring for further 30 minutes as it was, an aqueous solution of trimethylsulfoxonium bromide (11.5 g/60 ml) was further added thereto over 30 minutes. The mixture was stirred for further 3 hours as it was, followed by stirring overnight at a bath temperature of 15°C. The resulting precipitates were collected by filtration and dried to give a crude product of the title compound. To the crude product was added a 50% acetone aqueous solution. After heating at 35°C, the mixture was adjusted to pH 7.0 with concentrated hydrochloric acid. Then, acetone was added dropwise thereinto and the mixture was stirred overnight. The precipitated crystals were collected by filtration and dried, to give the title compound in a yield of 85%.Example 8 Synthesis of Methylcobalamin All the procedures in the present example were performed in the dark (under red light). To 390 ml of ion-exchanged water were added 3 0 g of cyanocobalamin, 2.1 g of cobalt chloride hexahydrate, and 22.5 ml of 2-butanone. While blowing nitrogen gas at the flow rate of 15 ml/min. in to the system, the mixture was heated in a water bath, to which an aqueous solution of sodium borohydride (12 g/60 ml) was added dropwise under stirring at the internal temperature of 30°C over 2 hours. After stirring for further 30 minutes as it was, an aqueous solution of trimethylsulfoxonium bromide (11.5 g/60 ml) was further added thereto over 30 minutes. The mixture was stirred for further 3 hours as it was, followed by stirring overnight at a bath temperature of 15°C. The resulting precipitates were collected by filtration and dried to give a crude product of the title compound. To the crude product was added a 50% acetone aqueous solution. After heating at 35°C, the mixture was adjusted to pH 7.0 with concentrated hydrochloric acid. Then, acetone was added dropwise thereinto and the mixture was stirred overnight. The precipitated crystals were collected by filtration and dried, to give the title compound in a yield of 86%.Example 9 Synthesis of Methylcobalamin All the procedures in the present example were performed in the dark (under red light). To 13 L of ion-exchanged water were added 1 Kg of cyanocobalamin, 70 g of cobalt chloride hexahydrate, and 750 ml of 2-butanone. After replacing the inside atmosphere of the system with nitrogen gas, the mixture was heated in a water bath, to which an aqueous solution of sodium borohydride (400 g/2 L) was added dropwise while keeping and stirring at the internal temperature of 35°C+/-5°C over 120 minutes. An aqueous solution of trimethylsulfoxonium bromide (383 g/2 L) was further added thereto over 30 minutes. The mixture was stirred for further 3 hours as it was, followed by stirring overnight at a bath temperature of 15°C. The resulting precipitates were collected by filtration and dried to give a crude product of the title compound. To the crude product was added a 50% acetone aqueous solution. After heating at 35°C, the mixture was adjusted to pH 7.0 with concentrated hydrochloric acid. Then, acetone was added dropwise thereinto and the mixture was stirred overnight. The precipitated crystals were collected by filtration and dried, to give the title compound in a yield of 87%.
| 85% |