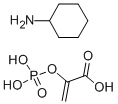
Phosphoenolpyruvic acid cyclohexylammonium salt CAS#: 10526-80-4; ChemWhat Code: 38345
Identification
Physical Data
| Appearance | White Powder |
| Melting Point, °C |
| 143 – 146 |
| 144 – 146 |
Spectra
No data available
Route of Synthesis (ROS)
| Conditions | Yield |
| (i) DCC, Py, (ii) /BRN= 1098229/; Multistep reaction; |
Safety and Hazards
| Pictogram(s) |  |
| Signal | Warning |
| GHS Hazard Statements | H315 (100%): Causes skin irritation [Warning Skin corrosion/irritation] H319 (100%): Causes serious eye irritation [Warning Serious eye damage/eye irritation] H335 (100%): May cause respiratory irritation [Warning Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure; Respiratory tract irritation] |
| Precautionary Statement Codes | P261, P264, P264+P265, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P319, P321, P332+P317, P337+P317, P362+P364, P403+P233, P405, and P501 (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
Other Data
| Transportation | Store at 2~8 ℃, Sealed and away from light. |
| HS Code | |
| Storage | Store at 2~8 ℃, Sealed and away from light. |
| Shelf Life | 1 year |
| Druglikeness | |
| Lipinski rules component | |
| Molecular Weight | 267.219 |
| logP | |
| HBA | 7 |
| HBD | 4 |
| Matching Lipinski Rules | 3 |
| Veber rules component | |
| Polar Surface Area (PSA) | 139.89 |
| Rotatable Bond (RotB) | 3 |
| Matching Veber Rules | 2 |
| Use Pattern |
| Phosphoenolpyruvate monocylohexylamine salt (PEP monocylohexylamine salt) is an important organophosphorus compound, primarily used in the fields of biochemistry and pharmaceutical research with the following applications: Substrate in Enzyme Reactions: Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) is a key intermediate in the glycolysis pathway. The monocylohexylamine salt form of PEP can be used in vitro to study substrate behavior in enzyme reactions, especially in research involving glycolysis or energy metabolism. Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxykinase (PEPCK) Studies: PEP is a critical substrate in reactions catalyzed by PEPCK, a key enzyme in the gluconeogenesis pathway. Studying this process is essential for understanding metabolism, diabetes, and other metabolic disorders. ATP Synthesis: In vitro ATP synthesis experiments often use PEP to provide phosphate groups, generating ATP through reactions with ADP. This is highly valuable for research on cellular energy metabolism. Drug Development and Biomedical Research: PEP monocylohexylamine salt may be used in the development of metabolism-related drugs, particularly for research targeting metabolic pathways associated with diseases such as cancer or diabetes. |
Buy Reagent | |
| No reagent supplier? | Send quick inquiry to ChemWhat |
| Want to be listed here as a reagent supplier? (Paid service) | Click here to contact ChemWhat |
Approved Manufacturers | |
| Want to be listed as an approved manufacturer (Requires approvement)? | Please download and fill out this form and send back to approved-manufacturers@chemwhat.com |
Contact Us for Other Help | |
| Contact us for other information or services | Click here to contact ChemWhat |